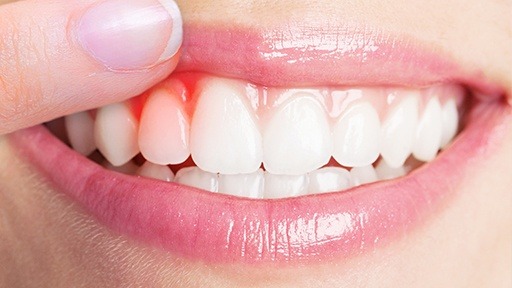
Bacteria or viruses invade and grow within the gums (soft tissues that surround the tooth), causing swelling, inflammation and susceptibility to bleeding.
Types:
- Gingivitis (Inflamed Gums): An inflamed gum with low immunity against bacteria. If left untreated, the surface of the gum will fall off, leaving behind unprotected gum tissues. Regular dental care visits (twice a year) and following the Bloom Dent Tips for Proper Mouth Cleaning will prevent Gingivitis.
- Causes of gingivitis:
- Diabetes and other medical conditions.
-Smoking decreases the ability of gum to heal, causing gingivitis.
-Dry mouth, due to old age, medication or psychological stress.
-Pregnancy Gingivitis: Due to the high levels of progesterone present in the body during pregnancy (likely to fade after delivery).
- Periodontitis (Inflamed Gum and Bone):
Periodontitis occurs when the swollen gums damage the bone underneath them. Antibiotics must be administered prior to treatment, and food accumulation at the root of the tooth is removed. In severe cases, surgery is needed to correct the distorted shape of the gums and bone tissues.
-
- Types of Periodontitis:
-Slight Periodontitis: The gingival (gum) inflammation progresses and starts to attack to the deeper (bone) tissues. This causes a slight bone loss.
-Moderate Periodontitis: Loss of bone and periodontal tissue is more noticeable.
-Severe Periodontitis: Breakdown of periodontal tissues with major loss of bone support. Tooth is loose and there is severe bad breath.
-Pericoronitis: The upper wisdom tooth bites onto gum tissue on top of un-erupted lower tooth, and the tissues become inflamed and invaded by bacteria. This condition is characterized by severe pain and difficulty in opening the mouth.
-Periodontal abscess: A ball of pus is formed within gum tissues, exerting pressure on bone and damaging it.